- Phone :+917814622609
- Email :civilstaphimachal@gmail.com
- Student Dashboard
CivlsTap Himachal, Himachal Pradesh Administrative Exam, Himachal Allied Services Exam, Himachal Naib Tehsildar Exam, Tehsil Welfare Officer, Cooperative Exam and other Himachal Pradesh Competitive Examinations.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
Environment Performance Index-2022, an international ranking system that measures environmental health and sustainability of countries
India’s Performance
- India was ranked last among 180 countries that have been ranked
- With a score of 18.9, India’s 180th ranking comes after Pakistan, Bangladesh, Vietnam and Myanmar — the bottom five together make up the poorest performing countries for environmental health.
- India has also scored low on rule of law, control of corruption and government effectiveness
- India was ranked 168th in EPI-2020, with a score of 27.6
About EPI
- The EPI, a biennial index, was started in 2002 as Environmental Sustainability Index.
- EPI is published by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with the Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy and the Columbia University Center for International Earth Science Information Network
- Using 40 performance indicators across 11 issue categories, EPI ranks 180 countries on climate change performance, environmental health, and ecosystem vitality.
- Top five rank holders this year are – Denmark, UK, Finland, Malta and Sweden
Findings of the report
- It has found that good policy results are associated with wealth, meaning economic prosperity makes it possible for nations to invest in policies and programmes that lead to desirable outcomes
- This is especially true under environmental health, as building the necessary infrastructure to provide clean drinking water and sanitation, reduce air pollution, control hazardous waste etc yields large returns for human well-being
- The report says that top-performing countries have paid attention to all areas of sustainability, while their lagging peers tend to have uneven performance.
- It highlights that countries making concerted efforts to decarbonize their electricity sectors have made the greatest gains in combating climate change, with associated benefits for ecosystems and human health.
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
The government of India, for the first time this year, will present a unified count of the tiger, leopard and elephant populations of the country.
Benefits of the new method:
Given that 90% of the area occupied by elephants and tigers is common, and once estimation methods are standardised, having a common survey can significantly save costs.
- Also, the ‘head count’ method, or one currently deployed to count elephants was “obsolete” and frequently led to animals being double counted.
How are they counted currently?
Currently, the tiger survey is usually held once in four years and elephants are counted once in five years.
- Since 2006, the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), Dehradun, which is affiliated to the Environment Ministry, has a standardised protocol in place that States then use to estimate tiger numbers. Based on sightings in camera traps and indirect estimation methods, tiger numbers are computed.
- Elephant numbers largely rely on States directly counting the number of elephants. In recent years, techniques such as analysing dung samples have also been deployed to estimate birth rates and population trends in elephants.
Numbers:
- According to the most recent 2018-19 survey, there were 2,967 tigers in India.
- According to the last count in 2017, there were 29,964 elephants in India.
Efforts aimed at conservation of Elephants and their corridors at all- India level:
- ‘Gaj Yatra’, a nationwide campaign to protect elephants, was launched on the occasion of World Elephant Day in 2017. The campaign is planned to cover 12 elephant range states.
- The campaign aims to create awareness about elephant corridors to encourage free movement in their habitat.
Forest Ministry guide to managing human-elephant conflict (Best Practices):
- Retaining elephants in their natural habitats by creating water sources and management of forest fires.
- Elephant Proof trenches in Tamil Nadu.
- Hanging fences and rubble walls in Karnataka.
- Use of chili smoke in north Bengal and playing the sound of bees or carnivores in Assam.
- Use of technology: Individual identification, monitoring of elephants in south Bengal and sending SMS alerts to warn of elephant presence.
Efforts by Private Organizations in this regard:
- Asian Elephant Alliance, an umbrella initiative by five NGOs, had, last year, come together to secure 96 out of the 101 existing corridors used by elephants across 12 States in India.
- NGOs Elephant Family, International Fund for Animal Welfare, IUCN Netherlands and World Land Trust have teamed up with Wildlife Trust of India’s (WTI) in the alliance.
About Asian Elephants:
- Asian elephants are listed as “endangered” on the IUCN Red List of threatened species.
- More than 60% of the world’s elephant population is in India.
- Elephant is the Natural Heritage Animal of India.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The West Bengal government’s decision to make the Chief Minister the Chancellor of State-run universities, instead of the Governor has refocused the attention on the Governor’s Role in Universities
- The area of conflict here are the appointment of Vice-Chancellors and the functioning of universities
- VCs were appointed by the Chancellor of the universities
Similar Instances:
Tamil Nadu
- Tamil Nadu recently passed Bills to empower the State government, instead of the Chancellor, to appoint VCs.
- It also passed a separate bill to establish a new university for alternative systems of medicine with the Chief Minister as its Chancellor.
Kerala
- In Kerala, the situation is different, with Governor asking the Chief Minister to take over the Chancellor’s role in the light of alleged political interference in the functioning of universities.
These developments underscore that the conferment of statutory roles to Governors may be a source of friction between elected regimes and Governors who are seen as agents of the Centre
Governor’s Role in
State Universities:
- In most cases, the Governor of the state is the ex-officio chancellor of the universities in that state.
- While the Governor’s powers and functions as the Chancellor are laid out in the statutes that govern the universities under a particular state government.
- Their role in appointing the Vice-Chancellors has often triggered disputes with the political executive.
Central Universities:
- Under the Central Universities Act, 2009, and other statutes, the President of India shall be the Visitor of a central university.
- Chancellors are appointed by the President in his capacity as Visitors.
- They are titular heads with their role limited to presiding over convocations in central universities.
- The VCs too are appointed by the Visitor from panels of names picked by search and selection committees formed by the Union government.
- The President, as Visitor, shall have the right to authorize inspections of academic and non-academic aspects of the universities and also to institute inquiries
The original intent of making Governors hold the office of Chancellor and vesting some statutory powers on them was to insulate universities from political influence
Sarkaria Commission
- Justice R.S. Sarkaria Commission noted the use of discretion by some Governors in some university appointments had come in for criticism.
- It acknowledged the distinction between the Governor’s constitutional role and the statutory role performed as a Chancellor, and also underlined that the Chancellor is not obliged to seek the government’s advice.
M.M. Punchhi Commission
- Noted that Governor should not be “burdened with positions and powers, which may expose the office to controversies or public criticism, it advised against conferring statutory powers on the Governor, it advised against conferring statutory powers on the Governor.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has published a fresh draft of amendments to the Information Technology Rules, 2021
What are the proposed amendments to the IT Rules, 2021?
- The draft proposes to create government-appointed appeal committees that will be empowered to review and possibly reverse content moderation decisions taken by social media companies.
- It means in case a user is not satisfied with the content moderation decision taken by a company’s grievance officer, they can appeal that decision before the proposed government-appointed appeals committee.
- Every order passed by the Grievance Appellate Committee shall be complied with by the concerned intermediary
- Currently, the only recourse a user has against companies’ content decisions is to approach the courts
- Responsibility on grievance officers appointed by social media companies – if a user complains about content which is “patently false”, infringes copyright, and threatens the integrity of India, among other things, a grievance officer will have to expeditiously address it within 72 hours.
- Under current rules, grievance officers have 15 days to act on and dispose of users’ complaints.
What prompted the amendments?
- The IT Rules, 2021 provide for a robust grievance redressal mechanism.
- However, there have been many instances that grievance officers of intermediaries either do not address the grievances satisfactorily and/or fairly.
- In such a scenario, the need for an appellate forum has been proposed to protect the rights and interests of users
Concerns
- The proposal, without any legislative basis, seeks to subject content on social media to the direct scrutiny of the government by permitting users to appeal decisions of social media platforms to a Grievance Appellate Committee constituted by MeitY
IT Rules, 2021
- These new rules deal with social media and over-the-top (OTT) platforms.
- These rules have been framed in exercise of powers under section 87 (2) of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000
New Guidelines for Social Media/Intermediaries:
Categories of Social Media Intermediaries:
- Based on the number of users, on the social media platform intermediaries have been divided in two groups:
- Social media intermediaries.
- Significant social media intermediaries.
Features
- In case, due diligence is not followed by the intermediary, safe harbor provisions will not apply to them.
- The safe harbor provisions have been defined under Section 79 of the IT Act, and protect social media intermediaries by giving them immunity from legal prosecution for any content posted on their platforms.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism is Mandatory:
- Intermediaries shall appoint a Grievance Officer to deal with complaints and share the name and contact details of such officers.
- The grievance Officer shall acknowledge the complaint within twenty-four hours and resolve it within fifteen days from its receipt.
Ensuring Online Safety and Dignity of Users:
- Intermediaries shall remove or disable access within 24 hours of receipt of complaints of contents that exposes the private areas of individuals, show such individuals in full or partial nudity or in sexual act or is in the nature of impersonation including morphed images etc.
Additional Due Diligence for the Significant Social Media Intermediaries:
- Appointments: Need to appoint Chief Compliance Officer, a Nodal Contact Person and a Resident Grievance Officer, all of whom should be resident in India.
- Rules for News Publishers and OTT Platforms and Digital Media:
For OTT:
- Self-Classification of Content: The OTT platforms, called as the publishers of online curated content in the rules, would self-classify the content into five age based categories- U (Universal), U/A 7+, U/A 13+, U/A 16+, and A (Adult).
- Parental Lock: Platforms would be required to implement parental locks for content classified as U/A 13+ or higher, and reliable age verification mechanisms for content classified as “A”.
- Display Rating: Shall prominently display the classification rating specific to each content or program together with a content descriptor informing the user about the nature of the content
For Publishers of News on Digital Media:
They would be required to observe Norms of Journalistic Conduct of the Press Council of India and the Programme Code under the Cable Television Networks Regulation Act 1995 thereby providing a level playing field between the offline (Print, TV) and digital media.
- Grievance Redressal Mechanism: A three-level grievance redressal mechanism has been established under the rules with different levels of self-regulation.
- Self-regulation by the Publisher:
- Publisher shall appoint a Grievance Redressal Officer based in India who shall be responsible for the redressal of grievances received by it.
- The officer shall take decision on every grievance received by it within 15 days.
- Self-Regulatory Body:
- There may be one or more self-regulatory bodies of publishers.
- Such a body shall be headed by a retired judge of the SC, a High Court or independent eminent person and have not more than six members.
- Such a body will have to register with the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting.
- This body will oversee the adherence by the publisher to the Code of Ethics and address grievances that have not been resolved by the publisher within 15 days.
Oversight Mechanism:
- Ministry of Information and Broadcasting shall formulate an oversight mechanism.
- It shall publish a charter for self-regulating bodies, including Codes of Practices. It shall establish an Inter-Departmental Committee for hearing grievances.
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
A group of environmentalists, lawyers, and activists have come together to identify and ‘defuse carbon bombs’– coal, oil and gas projects that have the potential to contribute significantly to global warming.
- The usage of the term ‘carbon bombs’ picked up after an investigative project of The Guardian
- The project reported the plans of countries and private companies all over the world to engage in 195 ‘carbon bomb’ projects.
- Each such project, will release huge amounts of CO2 emissions into the atmosphere.
What are carbon bombs?
- It is an oil or gas project that will result in at least a billion tonnes of CO2 emissions over its lifetime.
- Whenever coal, oil, or gas is extracted it results in pollution and environmental degradation.
- In total, around 195 such projects have been identified world over, including in the US, Russia, West Asia, Australia and India.
- These projects will collectively overshoot the limit of emissions that had been agreed to in the Paris Agreement of 2015.
What does the investigation say?
- More than 60% of these carbon bomb projects are already underway
- Apart from coal, oil, and gas operations, the report highlighted the threat of methane, which routinely leaks from gas operations and is a powerful greenhouse gas, trapping 86 times more heat than CO2 over 20 years
- The report criticized reliance on fuel from conventional sources and not making use of emerging, green sources of energy.
What is the plan for ‘defusing’ carbon bombs?
- The network working towards this goal is called Leave It In the Ground Initiative (LINGO).
- Its mission is to leave fossil fuels in the ground and learn to live without them.
- It believes the root of climate change is the burning of fossil fuels, and the 100% use of renewable energy sources is the solution.
- LINGO aims to organise ground support for protesting such projects, challenge them through litigation, and conduct analysis and studies for the same.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 1
The atmosphere of religious intolerance which has seen a sharp rise in the last several years has been a serious cause for concern in the country.
- India is the beloved home for practitioners of all major religions in the world. Indian culture accepts diversity of faiths and beliefs.
- Religious harmony and social cohesion are two core elements for progress and development.
- As per Pew Research Survey 2021, Indians of diverse religious backgrounds overwhelmingly say they are very free to practice their faiths
- But there is growing intolerance towards diverse religions leading to communal violence and ripples in social harmony.
Instances of intolerance
- Recent incident of ruling party spokesperson commenting on Islam and the Prophet
- Haridwar Hate speech incident
- Frequent use of National Security Act (NSA) for ‘cow slaughter’ by some state governments
- As per pew research on the question of inter-religious marriage, most Hindus (67%), Muslims (80%), Sikhs (59%), and Jains (66%) felt it was ‘very important’ to stop the women in their community from marrying outside their religion
Why is there raise in intolerance?
- Political parties polarize naive voters in the name of religion
- Various cultural organisations are misinterpreting and propagating truths to affirm revivalist predispositions
- Irresponsible Reporting by Media: Many a times media broadcasts unconfirmed, sensitive and often biased reports on national television
- For instance: Tablighi Jamaat case during first Covid lockdown
- State’s support: India has many hostile neighbors, who wish to make it weak through a communal divide.
- Struggle for identity
Consequences
- Threat to minority: Rise in intolerance and communal disharmony lead to majoritarianism
- Mob-violence: Rise in disharmony has led to targeting of religious minorities and led to a rise in mob-violence
- Threat to Rule of law: With rise in incidence of mob lynchings, there is a threat to rule of law – Lynching on cow smuggling, lynching of youth in golden temple
- Freedom of speech: It has also impacted freedom of speech-shows of comedians being banned by vigilante groups
- Regionalism: The anti-national elements get adequate opportunity to fan regional feelings and work on creating an atmosphere to break the cohesiveness of our society.
- Damage social fabric: The social fabric of the society gets irreparably damaged and the conditions of mistrust serve as a catalyst for future conflicts
- Degrading International image where countries are losing faith in India’s diverse credentials
Way forward
- Political and moral support to the minorities
- Effective administration – fair probe, media guidelines
- Implementation of constitutional and legal safeguards
We, the people of India, must strive hard to generate compassion, strength, sincerity and commitment to ensure the safety and security of the people of India. And uphold the values which are synonym with the word “INDIA” – tolerance, compassion and peace.
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
A Chinese base in Cambodia could become a choke-point in the Gulf of Thailand close to the strategically important Malacca Strait that has prompted global concern that it will be used by Beijing as a naval outpost on the Gulf of Thailand.
- Cambodia’s official described the expansion of the Ream Naval Base as “cooperation between China and Cambodia”
Background
- China and Cambodia have reportedly signed a secret pact allowing China exclusive use of a naval base on the Gulf of Thailand, although officials from both countries have denied such a deal exists.
Ream Naval Base
- Location: Ream Naval Base is a facility operated by the Royal Cambodian Navy on the coast of the Gulf of Thailand in the province of Sihanoukville, Cambodia.
- Ream faces the Gulf of Thailand, adjacent to the South China Sea
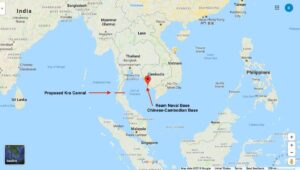
Significance
- This would be china’s second overseas naval foothold, after a base in Djibouti opened in 2017.
- A Chinese base in Cambodia could become a choke-point in the Gulf of Thailand close to the strategically important Malacca Strait.
- China’s strategic military footprint in Southeast Asia would help it bolster its territorial claims in the disputed South China Sea.
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The Assemblies of 4 states will elect 16 MPs to Rajya Sabha
- Rajya Sabha, or the Council of States, has 245 seats
- No ruling party has ever touched the 100 mark in the last three-and-a-half decades
- Every Rajya Sabha seat counts as any Bill, barring Money Bills, needs the assent of the second chamber to become law.
How often are Rajya Sabha elections held?
- Rajya Sabha is a permanent House and cannot be dissolved.
- To ensure continuity, one-third of its members retire after every second year, under Article 83(1) of the Constitution, and “biennial elections” are held to fill these vacancies.
- The term of a member is six years.
- Out of the 245 members, 12 are nominated by the President and 233 are representatives of the States and Union territories of Delhi and Puducherry.
Rajya Sabha polls: Who votes, and how?
- Rajya Sabha MPs are elected by MLAs through an indirect election.
- Article 80(4) provides that members shall be elected by the elected members of state Assemblies through a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
- The Fourth Schedule to the Constitution provides for allocation of Rajya Sabha seats to the states and Union Territories, on the basis of the population of each state.
How are the votes counted?
- The number of votes a candidate requires depends on the number of vacancies and the strength of the House.
- If there is only one vacancy, the required quota is calculated by taking the number of votes polled, divided it by 2, and adding 1.
- If there is more than one vacancy, the equation is based on an assigned value of 100 for every first-preference vote. The values of the votes credited to all candidates are total. The total is divided by 1 more than the number of vacancies, and 1 is added to this quotient.
- If for any seat, candidates fail to get the specified number, the second-preference votes will be taken into account, but with a lower value.
Beyond passing Bills, why do Rajya Sabha numbers matter?
Rajya Sabha enjoys some special powers
- It can pass resolution to enact laws on state subject
- Recommend creation of one or more All India Services common to the Union and the states
- Rajya Sabha has a role to play if the President proclamations national emergency, in the event of failure of constitutional machinery in a State, or in the case of financial emergency. Every such proclamation has to be approved by both Houses of Parliament within a stipulated period
- If a proclamation is issued at a time when Lok Sabha has been dissolved or the dissolution of Lok Sabha takes place within the period allowed for its approval, then the proclamation remains effective, if the resolution approving it is passed by Rajya Sabha within the period specified under Articles 352, 356 and 360 of the Constitution.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The Union Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) announced the country’s first National Air Sports Policy (NASP 2022).
- It has been launched to improve the state of aero sports in India, with a vision to make India a hub for air sports in the world by 2030.
- It aims to provide a safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable air sports ecosystem in India.
Highlights of the Policy
- Four-tier governance structure: The air sports in India will be under a four-tier governance structure. This includes: 1) Air Sports Federation of India (ASFI) as the apex governing body, 2) National associations for individual air sports or a set of air sports, 3) Regional or state and union territory level units of the national air sports associations and 4) District-level air sports associations.
- About ASFI: The ASFI will be an autonomous body under the Ministry of Civil Aviation and will represent India at the Lausanne-headquartered Fédération Aéronaautique Internationale (FAI) and other global platforms related to air sports. It will be chaired by the Secretary, Ministry of Civil Aviation.
- Functions: It will provide governance over various aspects of air sports, including regulation, certification, competitions, awards and penalties, etc.
- Rules and Functions of Each air sports association: Lay down its safety standards for equipment, infrastructure, personnel and training, and specify the disciplinary actions to be taken in case of non-compliance. Inability to do so may lead to penal action by the ASFI.
- Coverage: It will cover 13 air sports activities like aerobatics, aero-modelling, amateur-built and experimental aircraft, ballooning, drones, gliding, hang gliding, paragliding, microlighting, paramotoring, skydiving, and vintage aircraft.
Significance of the Policy:
- Besides the revenue from air sports activities, multiplier benefits in terms of growth in travel, tourism, infrastructure and local employment, especially in hilly areas of the country, are much greater.
- Creating air sports hubs across the country will bring in air sports professionals and tourists from across the world.
Need for:
The aerosports industry has expressed its displeasure that the government was not doing enough to encourage aero sports in the country despite the fact that there is a tremendous potential in the country keeping in view the diverse scenic locales.
- Aerosports create significant opportunities for growth of tourism, employment generation and interest in aviation activities.
- A growth-oriented NASP may help attract investments in latest aerosports technology, infrastructure and best practices.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
Petitioners in the Delhi High Court questioned why marital status, age, or gender were the criteria for being allowed to commission or not commission surrogacy in India.
Surrogacy Act, 2021
- The Act sought to regulate the surrogacy in India
- The Act defines ‘surrogacy’ as a practice where a woman undertakes to give birth to a child for another couple and agrees to hand over the child to them after birth
Why is there a need for a Surrogacy Act in India?
- India has emerged as a hub for infertility treatment, attracting people from the world due to prevailing socio-economic inequities, underprivileged women found an option to ‘rent their wombs’ and thereby make money to take care of their expenses
- By 2012, India had become the ‘surrogacy capital’ of the world with surrogacy tourism valued at approximately $500 million annually.
- Thus, it has become more than imperative to regulate surrogacy in the country.
- To curb unethical practices: Lack of specific legislation had led to unregulated growth of Commercial Surrogacy services. Hence, to curb unethical practices related to issues of sex selection and exploitation of the surrogate, specific legislation was required.
- To curb the exploitation of women: Due to the absence of legal regulations and lack of implementation, surrogate mothers faced multiple challenges – there had been many cases of death related to surrogacy which neither commissioning parents nor the doctors were ready to take responsibility of.
- Legal Issues: Sometimes, Indian adoption laws or citizenship laws of some other countries also create problems. For example, Germany gives citizenship by mother; this creates issues in determining the nationality of child.
- In 2008, a Japanese couple began the process with a surrogate mother in Gujarat, but before the child was born they split and there were no takers for the child.
- In 2012, an Australian couple commissioned a surrogate mother, and arbitrarily chose one of the twins that were born.
- Ethical Issues: Surrogacy leads to commoditization of the child. Renting of the womb breaks the bond between a mother and the child, interferes with nature
Key Provisions of the Act
- The Act prohibits commercial surrogacy, but allows altruistic surrogacy.
- Eligibility Criteria for Intending Couple: Any couple that has ‘proven infertility’ are candidates. The ‘intending couple’ as the Act calls them, will be eligible if they have a ‘certificate of essentiality’ and a ‘certificate of eligibility’ issued by the appropriate authority.
- Eligibility Criteria for Surrogate Mother: Only a close relative of the couple can be a surrogate mother, one who is able to provide a medical fitness certificate. She should have been married, with a child of her own, and must be between 25 and 35 years, but can be a surrogate mother only once.
- Appropriate Authority: The central and state governments shall appoint one or more appropriate authorities. The functions of the appropriate authority include;
- Granting, suspending or cancelling registration of surrogacy clinics;
- Enforcing standards for surrogacy clinics;
- National and State Surrogacy Boards: The central and the state governments shall constitute the National Surrogacy Board (NSB) and the State Surrogacy Boards (SSB), respectively.
- Parentage and Abortion of Surrogate Child: An abortion of the surrogate child requires the written consent of the surrogate mother and the authorization of the appropriate authority. This authorisation must be compliant with the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971.
- The surrogate mother will have an option to withdraw from surrogacy before the embryo is implanted in her womb.
What are the controversies behind the Act?
- Exclusion: The eligibility criteria for legally availing surrogacy excludes a chunk of society like unmarried females, LGBTQ+ persons, live-in couples, and single parents who wish to have surrogate child.
- Paternalistic: The altruistic model expects a woman to go through the physical and emotional tolls of surrogacy free of cost and only out of compassion.
- Autonomy of Woman: The banning of commercial surrogacy moves from the rights-based approach to a needs-based approach, thus removing the women’s autonomy to make their own reproductive decisions and right to parenthood.
- Limitations of Altruistic Surrogacy: Having a relative as a surrogate mother may lead to emotional complications. Altruistic surrogacy also limits the option of the intending couple in choosing a surrogate mother as very limited relatives
- Children with Disability: The Act considers having children with physical and special needs as childless. It further encourages considering surrogacy if the couple has a child with a life-threatening disorder. This clause directly violates the right of the children with the disability, thus denying them treatment with dignity.
As India is one of the major hubs of these practices, the Act is certainly a step in the right direction. More reforms are still needed recognize the rights of all stakeholders involved. The law needs to keep up with rapidly evolving demands of morality and societal changes.
Read More
© 2025 Civilstap Himachal Design & Development
