- Phone :+917814622609
- Email :civilstaphimachal@gmail.com
- Student Dashboard
CivlsTap Himachal, Himachal Pradesh Administrative Exam, Himachal Allied Services Exam, Himachal Naib Tehsildar Exam, Tehsil Welfare Officer, Cooperative Exam and other Himachal Pradesh Competitive Examinations.
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs approved computerisation of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) with the aim of increasing efficiency of PACS, bringing transparency and accountability in their operations.
- This project proposes computerization of about 63,000 functional PACS over a period of five years with a total budget outlay of Rs 2,516 crore with the central government’s share of Rs 1,528 crore.
Primary Agricultural Cooperative Credit Societies (PACS)
- The PACS constitute the lowest tier of the three-tier short-term cooperative credit (STCC) in India comprising of nearly 13 crore farmers as its members.
- Through computerization PACS will become nodal service delivery point for interest subvention scheme (ISS), PM Fasal Bima Yojana, Direct Benefit Transfer and provision of inputs like fertilisers, seeds etc.
- It will ensure speedy disposal of loans, lower transition cost, faster audit and reduction in imbalances in payments and accounting with State Cooperative Banks (SCBs) and District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs)
- PACS account for 41% of the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans given by all entities in the country and 95 % of these KCC loans through PACS are to the small and marginal farmers.
- The other two tiers viz. SCBs and DCCBs have already been automated by the NABARD and brought on Common Banking Software (CBS).
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The Enforcement Directorate has arrested Delhi Health Minister and senior Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) leader Satyendar Jain under the criminal provisions of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA) in connection with his alleged involvement in a ‘hawala transactions’ case.
About The Prevention of Money Laundering Act
It was enacted as a response to India’s global commitment (including the Vienna Convention) to curb the menace of money laundering.
Objectives of the Act: PMLA was enacted in 2002 and it came into force in 2005, to curb money laundering (process of converting black money into white) and to provide for seizure of property derived from money-laundering.
There are mainly 3 objectives of PMLA:
- To prevent and control money laundering.
- To confiscate and seize the property obtained from the laundered money.
- To deal with any other issue connected with money laundering in India.
Dispute Redressal
- The Adjudicating Authority is appointed by the central government. It decides whether the property attached or seized is involved in money laundering.
- The Adjudicating Authority shall not be bound by the procedure laid down by the Code of Civil Procedure,1908, but shall be guided by the principles of natural justice and subject to the other provisions of PMLA.
Appellate Tribunal: An Appellate Tribunal appointed by the Government is given the power to hear appeals against the orders of the Adjudicating Authority. Orders of the tribunal can be appealed in the appropriate High Court.
Special Court: Provision for establishing special court by the Union government under Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA).
PMLA (Amendment) Act, 2012:
- Adds the concept of ‘reporting entity’ which would include a banking company, financial institution, intermediary etc.
- PMLA, 2002 levied a fine up to Rs 5 lakh, but the amendment act has removed this upper limit.
- It has provided for provisional attachment and confiscation of property of any person involved in such activities.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 2
The Single Nodal Agency (SNA) Dashboard of PFMS (Public Financial Management System) was recently launched by the Union Ministry of Finance.
What is SNA Dashboard?
It is a major reform initiated in 2021 with regards to the manner in which funds for Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS) are released, disbursed and monitored.
- Under this system, each state is required to identify and designate an SNA for every scheme.
- All funds for that State in a particular scheme are now credited in this bank account and all expenses by all other Implementing Agencies involved are affected from this account.
Significance of SNA Model:
- Ensures timely allocation of funds.
- Brought in greater efficiency in CSS fund utilization.
- Tracking of funds has become easier.
About PFMS:
- It was previously known as Central Plan Schemes Monitoring System (CPSMS).
- It is a web-based online software application developed and implemented by the Office of Controller General of Accounts (CGA), Ministry of Finance.
- Objective: To facilitate a sound Public Financial Management System for the Government of India (GoI) by establishing an efficient fund flow system as well as a payment cum accounting network.
- Coverage: At present, the ambit of PFMS coverage includes Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes as well as other expenditures including the Finance Commission Grants.
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
The Agriculture Ministry unveiled India’s first Covid-19 vaccine for animals.
- Developed by the Hisar-based National Research Centre on Equines, the vaccine, called Ancovax, can protect animals against the Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
- This is the first Covid-19 vaccine for animals developed in India.
- There were reports from Russia last year that that country, too, had developed a vaccine against animals such as dogs, cats, minks, and foxes.
HOW IT WORKS
- Ancovax can be used in dogs, lions, leopards, mice, and rabbits.
- It is an inactivated vaccine developed using an infectious part of the Delta variant.
- In addition, it uses Alhydrogel as an adjuvant to boost the immune response.
THE NEED:
- There have been reports of Covid-19 infection in several animals, including dogs and cats.
- The vaccine can protect animals in the zoo.
- The animals develop similar symptoms to humans – cough, cold, fever, and lung lesions
- It can also prevent transmission from companion animals to the humans
- The aim of the vaccine is to protect endangered animals
Read More
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 1
British journalist and a Brazilian indigenous affairs expert recently went missing in a remote corner of the Amazon rainforest.
- The duo were last seen in Vale do Javari — the western section of the Brazilian Amazon named after the Javari river, which forms the country’s border with Peru.
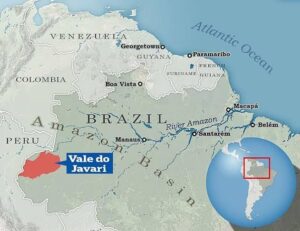
Why is the region significant?
- The region where Phillips and Pereira went missing is spread over 85,444 sq km and, according to the Brazilian government, it is home to “the greatest concentration of isolated groups in the Amazon and the world”.
- The area is home to 14 different indigenous tribes with nearly 6,000 inhabitants. These tribes are known to reject contact with the outside world.
- But in spite of that there are repeated attempts to forcibly enter their resource-rich territory.
- Vale do Javari also forms part of an international cocaine trafficking route, with gold being exchanged for drugs and arms, consequently making it a hotspot for violent crimes.
- Besides the Javari it is transected by the Pardo, Quixito, Itaquai and Ituí rivers.
- The Brazilian government has made it illegal for non-indigenous people to enter the territory
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
Leading global higher education analysts QS (Quacquarelli Symonds) has released the 19th edition of one of the most-consulted international university rankings.
- It is the only international ranking to have received the approval of International Ranking Expert Group (IREG).
How are institutions ranked?
QS uses six indicators to compile the ranking: Academic reputation (AR), employer reputation (ER), citations per faculty (CPF), faculty/student ratio, international faculty ratio and international student ratio.
Performance of Indian Institutions:
- The latest edition features 41 Indian universities, of which 12 improved their positions, 12 remained stable, 10 declined and seven are new entries.
- The IISc ranks 155th globally, and is the global leader in the citations per faculty (CpF) indicator, which QS uses to evaluate the impact of the research produced by universities.
- The IISc is the fastest rising South Asian university among the top-200 universities in the QS rankings, having climbed 31 places year on year.
- The IIT Bombay, which was the top Indian university in QS World University Rankings of the previous edition, is the second best Indian institution this time and climbed five places globally to reach the 172 rank.
- The third best Indian university is the Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi (IITD), followed by IIT Madras and IIT Kanpur.
- Jindal Global University is the top-ranked private institute in India.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 1
Prime Minister is all set to inaugurate The Astol Project that will provide tap water to 4.50 lakh people living in 174 tribal villages and 1,028 hamlets on the hills of Valsad district in Gujarat.
This is significant as the tribes in the area have been protesting against the central government’s Par-Tapi-Narmada Link Project.
Background:
Par-Tapi-Narmada river link project in south Gujarat was scrapped after strong protests by tribal communities of the three districts in the region.
About the Project:
- Envisioned under the 1980 National Perspective Plan.
- The project proposes to transfer river water from the surplus regions of the Western Ghats to the deficit regions of Saurashtra and Kutch.
It proposes to link three rivers:
- Par, originating from Nashik in Maharashtra and flowing through Valsad.
- Tapi from Satpura that flows through Maharashtra and Surat in Gujarat.
- Narmada originating in Madhya Pradesh and flowing through Maharashtra and Bharuch and Narmada districts in Gujarat.
Benefits:
The surplus water proposed to be diverted through the estimated Rs 10,211 crore Par-Tapi-Narmada link project is expected to irrigate an area of 2,32,175 hectares, of which 61,190 ha is en route to the link canal.
Why is this project being opposed?
According to a report by the NWDA, about 6065 ha of land area will be submerged due to the proposed reservoirs.
- A total of 61 villages will be affected, of which one will be fully submerged and the remaining 60 partly.
- The total number of affected families would be 2,509 of which 98 families would be affected due to the creation of the Jheri reservoir, the only one in Maharashtra, spread over six villages.
- In Gujarat, around 2000 families will be affected by the project. The districts where the project will be implemented are largely dominated, by tribals who fear displacement.
Benefits of interlinking:
- Enhances water and food security.
- Proper utilisation of water.
- Boost to agriculture.
- Disaster mitigation.
- Boost to transportation.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
Assam Rhino Estimation
Manas National Park – Status
- The current rhino population in the park was estimated at 40
- The park’s rhinos have a male-female sex ratio of 1:1, arrived at without considering 10 calves and five sub-adults
- The one-horned rhinos in Manas National Park, have an age structure pyramid, indicating higher life expectancy and significant growth in the population.
- There is no wider representation of calves and sub-adults to sustain the population structure
- Population pyramid for calves is clearly an indicative of a low birth rate, but is also suggestive of a lower death rate, which means that there is higher life expectancy
- But such a population may suffer losses if not supplemented through translocations, the report warned.
- A suitable strategy to bring in more rhinos from other rhino-bearing areas is required so as to have a wider representation of calves and sub-adults over time, the report stated
Counting limitations
- “Total count” or direct count method adopted for the population estimation in Manas has a few limitations.
- A total count is generally used when a single species is targeted to be counted in a well-defined, specific area.
- This method assumes the detection probability to be one, which means that each and every animal has a 100% chance of being seen during the counting.
- The limitations of this method include undercounting, as the assumption of a detection probability of 1 is unrealistic, especially if the population closure cannot be established satisfactorily within a small area of 10-20 sq. km.
Manas National Park:
- Manas national park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, a Project Tiger reserve, an elephant reserve and a biosphere reserve.
- It is located in the Himalayan foothills in Assam. It is contiguous with the Royal Manas National Park in Bhutan.
- The name of the park is originated from the Manas River.
- Significance: The Park is known for its rare and endangered endemic wildlife such as the Assam roofed turtle, hispid hare, golden langur and pygmy hog. It is also famous for its population of wild water buffalo.
- River: The Manas River flows through the west of the park. Manas is a major tributary of Brahmaputra river.
Syllabus: General Studies Paper 3
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development’s (Unctad) has released the annual World Investment Report.
Highlights of the Report: India 7th in FDI Inflows: UNCTAD
- India is ranked seventh despite a 30% decline in foreign direct investment (FDI) into the country.
- The United States ($367 billion) remained the top recipient of FDI.
- China ($181 billion) and Hong Kong ($141 billion) also retained second and third position respectively.
- Among the top 10 host economies, only India saw a decline in its inflows.
- However, outward FDI from India rose 43 per cent to $15.5 billion in 2021.
What is FDI?
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment from a party in one country into a business or corporation in another country with the intention of establishing a lasting interest. With FDI, foreign companies are directly involved with day-to-day operations in the other country.
About United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD):
- It is a permanent intergovernmental body established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1964.
- It is part of the UN Secretariat.
- It reports to the UN General Assembly and the Economic and Social Council, but has its own membership, leadership, and budget.
- It is also a part of the United Nations Development Group.
Objectives and roles:
- It supports developing countries to access the benefits of a globalized economy more fairly and effectively. Along with other UN departments and agencies.
- It also measures the progress made in the Sustainable Development Goals, as set out in Agenda 2030.
Reports published by UNCTAD
- Trade and Development Report
- World Investment Report
- Technology and Innovation Report
- Digital Economy Report
Read More
© 2025 Civilstap Himachal Design & Development
