- Phone :+917814622609
- Email :[email protected]
- Student Dashboard
CivlsTap Himachal, Himachal Pradesh Administrative Exam, Himachal Allied Services Exam, Himachal Naib Tehsildar Exam, Tehsil Welfare Officer, Cooperative Exam and other Himachal Pradesh Competitive Examinations.
General Studies Paper-2
Context: The United Nations’ goal to eradicate world hunger by 2030 seems increasingly challenging to achieve due to the impacts of wars, climate change, and economic crises.
About
- Goal 2 of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is all about creating a world free of hunger by 2030.
- The 2024 Global Hunger Index score for the world is 18.3, with 42 countries still experiencing alarming or serious hunger.
- Hunger is most severe in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia where the crisis has soared to humanitarian levels.
- Little progress has been made on reducing hunger since 2016, and the prospects for achieving Zero Hunger by the target date of 2030 are grim.
Food Insecurity in India
- India has been ranked 105th out of 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024, placing it in the “serious” category for hunger levels.
- The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023 report states that around 224 million people in India faced moderate or severe food insecurity in 2021-22.
What are the challenges?
- Wars and Conflicts: Ongoing conflicts like in the Red Sea, disrupt supply chains, and access to food, leading to severe hunger, especially in vulnerable regions like sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
- Climate Change: Extreme weather events, droughts, floods, and shifting agricultural patterns caused by climate change severely affect food production and availability.
- Regional Disparities: Hunger remains most severe in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, where conditions have escalated to humanitarian crises, making it harder to address hunger effectively in these regions.
- The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated food insecurity, pushing many households into poverty and making it harder for them to access sufficient food.
India’s Efforts to achieve zero hunger by 2030
- Mid-Day Meal Programme: The Programme aims to boost enrolment, retention, and attendance while improving the nutritional status of children in government, local body, and government-aided schools.
- Food Fortification: The government promotes fortified rice, wheat flour, and edible oils as part of the public distribution system.
- The National Food Security Act, 2013: The Act provides for coverage of upto 75% of the rural population and upto 50% of the urban population for receiving subsidized foodgrains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Poshan Tracker: The Ministry of Women and Child Development developed the Poshan Tracker ICT application as a key governance tool.
- It uses WHO’s expanded tables with day-based z-scores to dynamically assess stunting, wasting, underweight, and obesity in children based on height, weight, gender, and age.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana was launched to alleviate hardships faced by the poor due to economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 outbreak.
- SakshamAnganwadi and Poshan 2.0 includes key schemes such as the POSHAN Abhiyaan, Anganwadi Services and Scheme for Adolescent Girls as direct targeted interventions to address the problem of malnutrition in the country.
Way Ahead
- Humanitarian Assistance: Provide more financial resources for humanitarian aid to conflict-affected regions to ensure food distribution and nutritional support.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Promote agricultural practices that can withstand shocks from climate change.
- Targeted Assistance Programs: Develop targeted food assistance programs for vulnerable populations affected by conflicts, including cash transfers and food vouchers.
General Studies Paper-1
Context: The World Survey on the Role of Women in Development report released by UN Women highlighting the widening gender gap in social protection.
About
- The report reveals that an alarming two billion women and girls are without access to any form of social protection. This is putting at risk progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 5 (SDG 5).
- Gendered poverty: Women aged 25 to 34 are 25 percent more likely than men in the same age group to live in extreme poverty.
- Conflict and climate change continue to exacerbate this inequality, with women in fragile environments being 7.7 times more likely to live in extreme poverty compared to those in stable regions.
- Maternity protection: Globally, over 63 percent of women still give birth without access to maternity benefits, with the figure reaching 94 per cent in sub-Saharan Africa.
Indian Scenario
- Health and Nutrition: The National Family Health Survey (NFHS-5) reveals that 23.3% of women (15-49 years) are undernourished, and 57% of women are anemic.
- The Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) in India was 97 per 100,000 live births in 2023, down from 130 in 2014.
- Gendered Poverty: According to Oxfam, 63% of women in India face unpaid caregiving responsibilities, which limits their economic participation.
- Labor Force Participation: In India, only around 37% of women aged 15 years and above participate in the workforce (compared to about 73% of men).
- Gender Gap in Education: As per NFHS-5, 70.3% of females are literate, compared to 84.7% of males.
Reasons of Vulnerability of Women
- Cultural Expectations and patriarchal norms restrict women’s opportunities to participate in formal employment and hinders their access to economic independence.
- Educational Disparities: Cultural practices like early marriage, gender-based violence in schools, and lack of sanitation facilities disproportionately affect girls’ attendance and retention rates in education.
- Informal Sector Employment: A large percentage of women are employed in informal sectors, which are characterized by low wages, irregular hours, and lack of job security.
Government Initiatives
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP): Launched to address the declining child sex ratio and promote education and survival of the girl child.
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY): A maternity benefit scheme providing financial assistance to pregnant and lactating mothers to ensure safe delivery and proper nutrition.
- Ujjwala Scheme: Provides free LPG connections to women from below poverty line (BPL) households to reduce health issues caused by smoke from traditional chulhas.
- Poshan Abhiyaan: This mission aims to improve nutrition outcomes for children, pregnant women, and lactating mothers.
- Digital Literacy Programme for Women: It is part of Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) and empowers women to access e-governance services and financial platforms, helping them participate in the digital economy.
- One Stop Centre Scheme (Sakhi Centres), aims to facilitate women affected by violence with a range of integrated services under one roof such as Police facilitation, medical aid, legal aid and legal counseling, psycho-social counseling, temporary shelter, etc.
Way Ahead
- The poor condition of women is a product of deeply rooted patriarchal norms, discriminatory practices, economic inequalities, and lack of targeted policies that address the specific needs of women.
- Addressing these systemic issues requires a comprehensive approach that includes improving access to education, healthcare, and legal protections, while promoting gender-responsive social protection policies.
Gender budgeting is a critical tool for advancing gender equality, promoting women’s empowerment, and achieving inclusive and sustainable development in India.
Read MoreGeneral Studies Paper-2
Context: The Prime Minister of India recently addressed the 19th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
India’s Total Renewable Energy Capacity Crosses 200 GW Mark
Last updated on October 16th, 2024 Posted on October 16, 2024 by NEXT IAS Current Affairs Team 49
Context
- India has reached a significant milestone as the country’s total renewable energy capacity crosses the 200 GW (gigawatt) mark in 2024.
India’s Energy Basket
India’s Renewable Energy Capacity
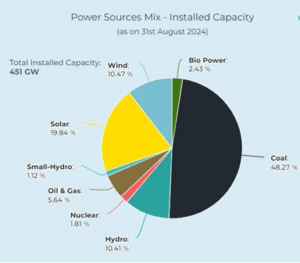
- India’s total electricity generation capacity has reached 452.69 GW.
- Having the 8,180 MW (megawatt) of nuclear capacity, the total non-fossil fuel-based power now accounts for almost half of the country’s installed electricity generation capacity.
- As of 2024, renewable energy-based electricity generation capacity stands at 201.45 GW, accounting for 46.3 percent of the country’s total installed capacity.
- Solar power contributes towards 90.76 GW, wind power follows closely with 47.36 GW, hydroelectric power generating 46.92 GW and small hydro power adding 5.07 GW, and biopower, including biomass and biogas energy, adds another 11.32 GW.

India’s Targets
- India has a vision is to achieve Net Zero Emissions by 2070, in addition to attaining the short-term targets which include:
- Increasing renewables capacity to 500 GW by 2030,
- Meeting 50% of energy requirements from renewables,
- Reducing cumulative emissions by one billion tonnes by 2030, and
- Reducing emissions intensity of India’s gross domestic product (GDP) by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
Challenges in Renewable Energy
- High Upfront Costs: The initial investment for renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar panels and wind turbines, is significant, which can be a barrier for many regions and investors.
- Geographical Disparities: Renewable resources are unevenly distributed, with some regions having limited access to wind or sunlight. This geographical imbalance can limit the feasibility of renewable energy adoption in certain areas.
- Governance Issue: Inconsistent government policies, regulatory challenges, and bureaucratic delays can slow down project approval and implementation, creating uncertainty for investors and developers.
- Infrastructure Development: The transition to renewable energy requires significant infrastructure development.
- The speed and scale of this infrastructure development can be a challenge for a country as large and diverse as India.
- Grid Integration: Integrating renewable energy into the existing power grid is a complex task.
- The grid must be flexible and capable of handling fluctuations in supply.
Steps Taken by Government for Transition to Renewable Energy Sources
- National Solar Mission (NSM): It was launched in 2010, it has set ambitious targets for solar capacity installation, including grid-connected and off-grid solar power projects.
- Green Energy Corridors: The Green Energy Corridor project focuses on enhancing the transmission infrastructure to facilitate the integration of renewable energy into the national grid.
- National Wind Energy Mission: Focuses on the development and expansion of wind energy in India. The target for wind energy capacity is set at 140 GW by 2030.
- National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF): It was established to support research and innovation in clean energy technologies and projects that help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO): This requires power distribution companies and large electricity consumers to procure a certain percentage of their power from renewable sources, encouraging the demand for renewable energy.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM-KUSUM): It includes the installation of solar pumps, solarization of existing grid-connected agricultural pumps, and the establishment of solar power plants on barren or fallow land.
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): India played a key role in establishing the International Solar Alliance, a coalition of solar-resource-rich countries to address their energy needs through the promotion of solar energy.
Conclusion
- This accomplishment is a testament to the nation’s commitment to a sustainable energy future including solar, wind, hydro, and bioenergy.
- With ambitious targets set for the future, India is well-positioned to emerge as a global leader in renewable energy, contributing to environmental sustainability and energy security.
- These ongoing efforts reflect a holistic approach to building a greener economy, ensuring that India not only meets its energy needs but also addresses the pressing challenges of climate change and resource conservation.
General Studies Paper-1
Context: Global warming is raising sea levels and making flooding more common in some areas.
- Researchers have held them responsible for discouraging the growth of plants of many tree species in coastal areas.
About
- The study paper has reported that a rising sea and coastal flooding could actually enhance the resilience of some coastal tree species while being detrimental to others.
- One species in particular, the American holly (Ilex opaca), responded by increasing the rate at which it grew — while loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) and pitch pine (Pinus rigida) trees suffered under higher water levels.
- Cause: The tree rings consist of water vessels. When a tree is exposed to a lot of rain along with appropriate levels of sunlight and ambient temperature, it also develops more water vessels.
- But a heavy downpour and a deluge would disrupt this process altogether and prevent the plant from growing normally.
Sea-level Rise Accelerating
- Sea levels were increasing by around 2 mm/year in 1993.
- This rate has since doubled and climate researchers expect floods in coastal areas will increase threefold by 2050.
- Reason: Climate change brought on by fossil-fuel burning and greenhouse gas emissions has led to a steady increase in global temperatures.
- As a result, sea surface temperatures and glacier melting have increased, eventually rising sea levels and posing a major threat to coastal cities worldwide, including Indian coastal cities.
Concerns with Increase in Sea Level
- Flooding: It leads to more frequent and severe flooding in coastal areas, threatening infrastructure, homes, and livelihoods.
- Displacement: Rising seas force communities to relocate, leading to displacement and potential conflicts over resources.
- Saltwater Intrusion: Salinity contaminate freshwater sources, affecting drinking water supplies and agriculture.
- Economic Impact: Coastal industries, such as fishing and tourism are severely impacted, leading to job losses and economic instability in affected regions.
- Biodiversity Loss: Ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs are threatened, impacting biodiversity and the services these ecosystems provide.
- Health Risks: Flooding leads to the spread of waterborne diseases.
India’s Efforts to Combat Climate Change
- Renewable Energy Expansion: India has set ambitious targets for renewable energy generation, aiming to increase its capacity significantly.
- It has invested heavily in solar and wind energy projects, with the goal of reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
- International Commitments: India is a signatory to the Paris Agreement, committing to reduce its carbon intensity and increase the share of non-fossil fuel energy sources in its total energy mix.
- It has announced its aim to meet 50% of its electricity demands from renewable energy sources by 2030.
- Afforestation and Forest Conservation: Recognizing the role of forests in carbon sequestration and climate regulation, India has initiated programs to increase forest cover, restore degraded lands, and promote sustainable forest management practices.
- Clean Transportation: India is promoting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and has set a target of 30% EV market share by 2030.
- The government has introduced incentives and subsidies to support the production and adoption of EVs.
- Climate Resilience: India is investing in measures to enhance climate resilience and adaptation, particularly in vulnerable sectors such as agriculture, water resources, and coastal areas.
- International Cooperation: India actively participates in international forums and collaborations on climate change, engaging in initiatives such as the International Solar Alliance and the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure.
General Studies Paper-2
Context: The Prime Minister of India recently addressed the 19th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
Key Highlights
- The PM emphasized that a free, open, inclusive, prosperous and rule-based Indo-Pacific is important for the peace and progress of the entire region.
- India stressed that maritime activities should be conducted under the UN Convention on the Law of the Seas (UNCLOS) to ensure freedom of navigation and air space.
- Also a strong and effective Code of Conduct should be created.
East Asia Summit (EAS)
- Origin: The origins of EAS dates back to the 1990 proposal for an East Asian Economic Grouping (EAEG).
- The project was later revived through the ASEAN Plus Three or APT (China, Japan, and South Korea) Summit of Heads of State and Government that first met in Kuala Lumpur in December 1997.
- It eventually found expression through the creation of the EAS in 2005, with 16 members. The United States and Russia joined in 2011.
- Members: There are 18 members;
- The 10 ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) members: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam.
- 8 non-ASEAN members: Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Russia, South Korea, and the United States.
- Lead & the Chair position: ASEAN leads the forum, and the chair position rotates between ASEAN Member States annually.
Significance of East Asian region
- Economic Growth: East Asia is home to some of the world’s largest and fastest-growing economies, including China, Japan, and South Korea.
- The region is known as the factory of the world.
- Diplomatic Hotspot: As a zone of interaction for major global powers like the US, China, and Russia, the region is critical for international diplomacy and geopolitical negotiations, influencing global peace and stability.
- Great Power Rivalries: East Asia is a focal point for great power competition, particularly between the United States and China. The region plays a key role in shaping the dynamics of global power and influence.
- Strategic Waterways: The region includes vital shipping lanes such as the South China Sea and the East China Sea, where disputes over territorial claims add to its geopolitical importance.
Challenges
- Territorial Disputes: Ongoing territorial disputes in the South China Sea and East China Sea involve multiple countries, including China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Japan, and Taiwan, leading to increased military tensions and instability.
- Regional Alliances: The emergence of military alliances and partnerships in the region, such as the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) involving the US, Japan, Australia, and India, complicates India’s relations with its neighbors and other East Asian countries.
- Regional Trade Agreements: India’s decision to opt out of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) limits its access to East Asian markets.
Way Ahead
- India’s engagement with the East Asian region is characterized by a complex interplay of opportunities and challenges in the realm of international relations.
- Navigating geopolitical rivalries, economic competition, and diverse political landscapes requires a multifaceted approach, balancing national interests with the necessity of fostering cooperative and constructive relationships in this strategically vital region.
General Studies Paper-2
Context: India decided to withdraw its High Commissioner and other affected diplomats and officials from Canada.
India-Canada Bilateral Relations
- Foundation of Ties: India-Canada relations are based on shared values of democracy, cultural diversity, economic engagement, and people-to-people connections.
- High-Level Exchanges: In 2015, PM Modi visited Canada, leading to multiple agreements.
- In 2018, Trudeau visited India, signing six agreements in various sectors.
- COVID-19 Cooperation: Leaders discussed vaccine collaboration and evacuation of stranded citizens.
- G-7 Meeting (2022): The two PMs met to enhance bilateral relations.
- G20 Summit (2023): Trudeau attended the summit in India and met Modi.
- Bilateral Mechanisms: Established dialogues in trade, energy, and foreign affairs, with recent consultations in 2023.
- Security Cooperation: Counter-terrorism efforts under a Joint Working Group established in 1997.
- Civil Nuclear Cooperation: An agreement signed in 2010 for peaceful nuclear energy uses, with implementation oversight by a Joint Committee.
- Energy Cooperation: Expanded Ministerial level Energy Dialogue since 2018 to include renewables.
- Space Collaboration: MoUs signed for satellite tracking and astronomy; ISRO has launched Canadian satellites.
- Economic Relations: Total bilateral trade in 2023 reached USD 9.36 billion, with significant service trade.
- Canadian investments in India exceed CAD 75 billion, with over 600 Canadian companies operating in India
- Exports: Pharmaceuticals, electronic goods, jewelry, seafood, engineering goods.
- Imports: Minerals, pulses, potash, and chemicals.
- Science and Technology Cooperation: Multiple MoUs signed for research and technological collaboration.
- Education: Largest foreign student demographic in Canada is Indian, with around 427,000 students.
- People-to-People Relations: Canada has a significant Indian diaspora (approximately 1.8 million), contributing to its economy and society.
- Cultural Exchanges: Co-production agreements in films and joint initiatives between Canada Post and India Post.
- ICCR chairs established at various Canadian universities to foster cultural cooperation.
Diplomatic row
- In September 2023, Canadian PM Trudeau alleged Indian involvement in the murder of Hardeep Singh Nijjar, which India rejected.
- India advised its nationals in Canada and suspended visa services for Canadians.
- Visa Resumption: Services resumed in specific categories in October and e-visas for certain categories in November 2023.
- The Ministry of External Affairs said the “unsubstantiated allegations” sought to shift focus away from “Khalistani terrorists and extremists who have been provided shelter in Canada”.
- Concerns were raised about the safety of Indian diplomats, stating that the Trudeau Government’s actions contribute to an atmosphere of extremism and violence
Future Outlook
- The Government of India strongly rejects preposterous imputations and ascribes them to the political agenda of the Trudeau Government that is centered around vote bank politics
- India indicated it reserves the right to take further actions in response to what it perceives as the Trudeau Government’s support for extremism and violence against India.
General Studies Paper-2
Context: Nearly a year after Maldives President election, Mohamed Muizzu made his first bilateral visit seen as an attempt to mend fences with India, and the Prime Minister of India ensured that India is always the ‘first responder’ for the Maldives in times of need.
New Beginnings and Old Complexities in India-Maldives Ties
- The relationship between India and the Maldives has always been a blend of strategic cooperation and occasional friction.
Recent Developments
- The election of President Mohamed Muizzu marked a turning point in Maldives-India relations. Initially, Muizzu’s ‘India Out’ campaign rhetoric created tensions, but recent diplomatic efforts have aimed at mending these ties.
- It had vowed to change the Maldives’s ‘India First’ policy adopted under his predecessor Solih and remove Indian military personnel from the island nation.
- Additionally, After election result, his decision to visit Turkey, China, and the UAE before India further complicated matters
- President Muizzu’s visit to India and subsequent high-level discussions with Indian officials, including the Prime Minister, have paved the way for renewed cooperation.
Economic and Strategic Cooperation
- India has extended substantial economic support to the Maldives, including a $100 million subscription to Maldivian T-bills and a ₹3,000 crore currency swap arrangement. These measures are crucial for stabilising the Maldivian economy and managing its debt.
- Additionally, both nations have announced new joint infrastructure projects and are exploring a Free Trade Agreement, highlighting the economic interdependence between the two countries.
Defence and Security
- Security remains a critical aspect of India-Maldives relations. India’s military presence in the Maldives has been a contentious issue, with calls for the replacement of Indian troops with technical personnel. It aims to address Maldivian concerns while maintaining security cooperation.
- The strategic location of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean makes it a vital partner for India in ensuring regional stability and countering external influences, particularly from China.
Tourism and Investment
- Tourism is a cornerstone of the Maldivian economy, and India plays a significant role as a source market. President Muizzu’s visit to Agra, Mumbai and Bengaluru underscored the importance of Indian tourists and investors.
- Efforts to restore pre-pandemic tourist levels and attract Indian investments are crucial for the Maldives’ economic recovery.
China’s growing influence in the Maldives
- Geopolitical Competition: The Maldives’ strategic location in the Indian Ocean makes it a key player in the geopolitical rivalry between India and China. China’s increasing presence in the Maldives, through infrastructure projects and financial aid, challenges India’s traditional influence in the region.
- Economic Dependencies: China has invested heavily in the Maldives, particularly through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). These investments include major infrastructure projects like the Sinamalé Bridge and the expansion of Malé International Airport.
- While these projects boost the Maldivian economy, they also increase the Maldives’ debt to China, raising concerns about a potential ‘debt trap’.
- Security Concerns: China’s involvement in the Maldives extends to security cooperation, which can be seen as a counterbalance to India’s military presence. It creates tension, as India views the Maldives as part of its strategic sphere of influence and is wary of Chinese military activities in the region.
- Political Shifts: Changes in the Maldivian government often lead to shifts in foreign policy that can strain Maldives-India relations, especially when new agreements with China are perceived as undermining India’s interests.
- Public Sentiment and Diplomacy: The Maldivian public and political factions are divided on the issue of foreign influence. While some view China’s investments as beneficial, others are concerned about sovereignty and the long-term implications of Chinese debt. This division influences the diplomatic strategies of both India and China in the Maldives
India’s Multifaceted Strategy To Counter China
- Strengthening Regional Alliances: India actively engages with neighbouring countries to build strong bilateral relationships. It includes economic aid, infrastructure projects, and diplomatic support.
- For instance, India has enhanced its ties with countries like Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Nepal to counterbalance China’s influence.
- Strategic Partnerships: India collaborates with like-minded countries through multilateral forums and strategic partnerships. The QUAD (comprising India, the US, Japan, and Australia) is a key example, where these nations work together to ensure a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
- Military Modernisation: India is modernising its military capabilities to deter any potential threats from China. This includes upgrading its naval and air forces, enhancing border security, and conducting joint military exercises with allies.
- Economic Initiatives: India promotes regional economic integration through initiatives like the SAARC and the BIMSTEC. These efforts aim to create economic interdependence that can counter China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Infrastructure Development: India invests in infrastructure projects in neighbouring countries to provide alternatives to Chinese investments. This includes building roads, ports, and railways that enhance connectivity and economic growth in the region.
- Diplomatic Engagement: India engages in proactive diplomacy to address regional concerns and build goodwill. This includes high-level visits, cultural exchanges, and people-to-people connections to strengthen ties with neighbouring countries
Conclusion
- The turnaround in Maldives-India relations is a testament to the power of subtle diplomacy over muscular posturing. It underscores the importance of sensitive and nuanced engagement in international relations.
- As Prime Minister Modi aptly put it, India remains the ‘first responder’ for the Maldives in times of need, reaffirming the deep-rooted ties between the two nations.
General Studies Paper-3
Context: India has been ranked 105th out of 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024, placing it in the “serious” category for hunger levels.
What is the Global Hunger Index (GHI)?
- GHI is a tool for comprehensively measuring and tracking hunger at global, regional, and national levels.
- The index is published by Concern Worldwide, an Irish humanitarian organisation, and Welthungerhilfe, a German aid agency.
Findings of the GHI 2024
- The 2024 Global Hunger Index score for the world is 18.3, considered moderate, down only slightly from the 2016 score of 18.8.
- Little progress has been made on reducing hunger since 2016, and the prospects for achieving Zero Hunger by the target date of 2030 are grim, with 42 countries still experiencing alarming or serious hunger.
- The wars in Gaza and Sudan have led to exceptional food crises.
- Somalia, Yemen, Chad, and Madagascar are the countries with the highest 2024 GHI scores; Burundi and South Sudan are also provisionally designated as alarming.
- Progress has been notable for example in Bangladesh, Mozambique, Nepal, Somalia, and Togo, although challenges remain.
- India’s performance remains concerning, in comparison to the South Asian neighbours such as Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, which fall into the “moderate” category.
- India is listed alongside countries like Pakistan and Afghanistan, which also face severe hunger challenges.
- The report reveals alarming statistics:7 percent of India’s population is undernourished, 35.5 percent of children under five are stunted, 18.7 percent suffer from wasting, and 2.9 percent of children die before their fifth birthday.
Policy Recommendations
- Strengthen accountability to international law and enforce the right to food.
- Promote gender-transformative approaches in food and climate policies.
- Invest in gender, climate, and food justice, ensuring public resources address inequalities.
Initiatives by Government of India to address Hunger
- Mid Day Meal Programme: It is a flagship programme of the Government of India aiming at enhancing enrolment, retention and attendance and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among children studying in Government, Local Body and Government-aided primary and upper primary school areas across the country.
- The National Food Security Act, 2013: The Act provides for coverage of upto 75% of the rural population and upto 50% of the urban population for receiving subsidized foodgrains under Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS), thus covering about two-thirds of the population.
- The Act also has a special focus on the nutritional support to women and children.
- Poshan Tracker: The Ministry of Women and Child Development developed and deployed the ‘Poshan Tracker’ ICT Application as an important governance tool.
- The Poshan Tracker has incorporated WHO’s expanded tables, which provide day-based z-scores, to dynamically determine stunting, wasting, underweight, and obesity status based on a child’s height, weight, gender, and age.
- The Central Government launched Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY) with the specific purpose of ameliorating the hardships faced by the poor and needy due to economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 outbreak in the country.
- The allocation of free food grains under PMGKAY was in addition to normal allocation done under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 (Mission Poshan 2.0) includes key schemes such as the POSHAN Abhiyaan, Anganwadi Services and Scheme for Adolescent Girls as direct targeted interventions to address the problem of malnutrition in the country.
- The beneficiaries under the Anganwadi Services scheme are children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Supplementary nutrition is provided to beneficiaries in the form of Hot Cooked Meals at Anganwadi Centres and Take Home Ration (not raw ration).
General Studies Paper-2
Context: The recent decision by the UK to transfer the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius marks a significant moment in both international relations and maritime geopolitics.
- This move addresses long-standing colonial legacies while reshaping the strategic landscape of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), particularly for countries like India, the UK, and the US.
Resolution of a Colonial Legacy
- Historical Context:
- The Chagos Archipelago has been a point of contention for decades. The sovereignty dispute arose from the forced displacement of Chagossians and the UK’s retention of the islands after Mauritius’ independence in 1968.
- International Pressure:
- The UK’s decision was heavily influenced by mounting pressure from various global bodies, including the International Court of Justice (ICJ) and the UN General Assembly, both of which had called for decolonization and the return of the islands to Mauritius.
- India has been a vocal advocate of this process, aligning with its broader decolonization agenda and supporting Mauritius’ claims.
Strategic Implications of the Transfer
- US-UK Interests:
- While sovereignty has been transferred, the deal preserves the US-UK control of the Diego Garcia military base for the next 99 years, ensuring both nations maintain their strategic foothold in the region.
- Diego Garcia is a vital base for US military operations, particularly in the Western Indian Ocean, and is critical for US nuclear submarines and naval logistics.
- India’s Role:
- As the principal security provider in the Eastern Indian Ocean, India views the development from both a tactical and strategic perspective.
- On the one hand, enhanced access to Diego Garcia could provide valuable operational advantages for India’s Navy, such as maritime patrolling, anti-piracy operations, and intelligence gathering.
- However, India’s proximity to the US military’s prime base in the Indian Ocean raises concerns about strategic autonomy.
- Historically, India has maintained a balance in its foreign policy and avoided being seen as aligning too closely with any single global power.
Challenges to India’s Strategic Autonomy
- Balancing Relations:
- India’s long-standing policy of strategic autonomy faces new challenges with the Diego Garcia development.
- Enhanced cooperation with the US could be perceived as a tilt toward the Western bloc, complicating India’s relationships with other key partners, such as Russia, Iran, and the Middle East.
- This could strain ties, especially given the US-Israel alliance and rising tensions with Iran, a significant partner for India in terms of energy and strategic interests.
- China’s Presence in the Indian Ocean:
- The transfer also needs to be viewed through the lens of China’s growing influence in the Indian Ocean.
- China has established a naval base in Djibouti and is expected to develop additional bases in Pakistan.
- India is thus concerned about China’s increasing maritime activities and its efforts to establish a dominant naval presence in the region.
India’s Opportunity in the Indian Ocean Region
- Collaboration with Mauritius:
- The sovereignty transfer offers India an opportunity to enhance maritime cooperation with Mauritius.
- India can assist in capacity-building efforts, particularly in monitoring Mauritius’ Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and protecting its maritime assets from threats like illegal fishing, often associated with Chinese vessels.
- Strengthening Mauritius’ maritime security is in India’s interest, as it can help mitigate China’s influence in the region without direct confrontation.
- Wider Representation:
- The agreement positions India to collaborate with Mauritius on maritime security, enhancing its influence in the Western Indian Ocean and counterbalancing China’s expanding role.
- India will need to do this while maintaining its independent status and avoiding alignment with the Western political agenda in the Middle East.
Geopolitical Calculations
- India’s Geopolitical Strategy:
- India must tread carefully to protect its interests without appearing overly aligned with Western powers.
- While India welcomes the continuation of US control over Diego Garcia—due to its close military ties with the US—New Delhi will likely adopt a measured response to ensure it retains its non-aligned image.
- Global South Leadership:
- By supporting Mauritius’ sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago, India reinforces its leadership role in the Global South and its commitment to decolonization.
- This strengthens its diplomatic standing and ensures India remains a key player in Indian Ocean geopolitics.
Conclusion
- The transfer of the Chagos Archipelago to Mauritius marks a significant turning point in the Indian Ocean’s strategic landscape. By collaborating with Mauritius on maritime security, India can enhance its presence in the Western Indian Ocean while maintaining its image as an independent regional power.
General Studies Paper-3
Context: Introduction to India’s AI Era
- The world is rapidly adapting to artificial intelligence (AI), and India stands on the cusp of a transformative era.
- The Indian economy is poised to grow at an average rate of 7% over the next five years, outpacing the global growth forecast of 3.2% for 2024.
- Hosting G20 and the Global Partnership on AI meetings in 2023 has created a favorable geopolitical environment for India to lead in AI adoption and innovation.
India’s AI Market Growth
- India’s AI market is expected to reach $17 billion by 2027, growing at an annualized rate of 25-35% between 2024 and 2027, according to Nasscom.
- India leads in generative AI (GenAI) adoption among 13 Asia-Pacific countries, as highlighted by Deloitte’s report.
- The Indian government has committed Rs 10,372 crore over five years to support the India AI Mission, further solidifying its position as a global AI leader.
AI’s Potential for Transformative Impact
- Historically, industries like electricity and automobiles witnessed transformation through visionary leadership (e.g., General Electric, Ford).
- Similarly, India’s AI ecosystem can drive sectoral transformations, providing inclusive economic growth and innovation.
- Indian industries need a tailored AI strategy, specific to sectoral challenges, to harness AI’s full potential.
Sectoral Example: Logistics Transformation
- The Indian logistics sector, previously riddled with inefficiencies, has witnessed transformations with traditional AI, bringing automation, optimization, and basic forecasting.
- Companies like PandoAI consolidated supply chain data to offer valuable analytics to Fortune 500 companies.
- GenAI can take the logistics sector further by uncovering hidden patterns, predicting disruptions, and designing innovative solutions, potentially reducing logistics costs (which are currently 7.8-8.9% of GDP).
Key to AI Success: Research, Development, and Infrastructure
- For India to lead in AI, businesses must invest in core compute capabilities, talent, and infrastructure.
- Despite producing 20% of the world’s data, India hosts only 2% of global data centers, limiting its AI computing capacity.
- The Indian government plans to enhance computational capabilities by procuring 10,000 graphics processing units (GPUs) and aims to build a domestic chip industry with over $10 billion in incentives under the National Semiconductor Mission.
Investment in Talent Development
- Hiring AI talent in India increased by 16.8% in 2023, highlighting the growing focus on AI capabilities.
- While many Indian-origin leaders contribute to global AI developments, a significant number work for international companies.
- Initiatives like Future Skills PRIME, a partnership between industry and government, need further support to develop a robust domestic AI workforce.
Establishing Trustworthy AI Standards
- Building trust in AI systems is crucial. Challenges such as data security, and ethical use, cybersecurity and data privacy concerns in the digital age.
- Robust governance frameworks are essential for addressing these issues, ensuring that AI is widely accepted and operates safely.
- India has the potential to influence global AI standards and policies due to its economic and geopolitical stature.
Key Government Initiatives Supporting AI in India
- National AI Strategy (NITI Aayog)
- Aim: To promote the adoption of AI in various sectors and make India a global leader in AI development.
- Focus Areas: Healthcare, agriculture, education, smart cities, and smart mobility.
- India AI Mission
- Aim: To develop an ecosystem that fosters AI innovation and research while ensuring its responsible use.
- National Programme on AI (Ministry of Electronics and IT – MeitY)
- Aim: To establish AI centers of excellence across the country and support AI-driven research and development.
- Initiatives under the Program:
- Centre of Excellence (CoEs): Setting up AI CoEs in major cities to encourage innovation and entrepreneurship.
- AI R&D Grants: The program provides funding for research projects in AI, particularly in areas like language translation, AI for healthcare, and smart cities.
- FutureSkills PRIME (NASSCOM & Ministry of Electronics and IT)
- Aim: To develop digital skills among professionals and students, particularly in AI, machine learning, cloud computing, and cybersecurity.
- National Supercomputing Mission (NSM)
- Aim: To enhance India’s computing power by building a network of high-performance computing systems.
Operationalizing India’s AI Ambition
- To fully harness AI’s transformative power, companies must take several key steps:
- Develop robust governance frameworks addressing ethics, data security, and bias.
- Ensure transparency in AI algorithms and decision-making.
- Promote inclusive AI development by incorporating diverse perspectives.
- Invest in ethical AI research through collaborations with academic and research institutions.
Strategic Vision for India’s AI Future
- A strategic commitment from the government and industry towards AI development has set the stage for India to emerge as a global leader.
- AI offers India the chance to drive economic growth, innovation, and inclusivity, positioning it at the forefront of global AI advancements.
Way Forward:
- India should deepen collaborations with leading AI nations like the US, Japan, and the EU to share best practices, access cutting-edge AI research, and jointly develop AI standards.
- Government-backed AI adoption grants and subsidies can enable SMEs to integrate AI into their business processes, enhancing their productivity and competitiveness.
- Industries such as healthcare, agriculture, logistics, and manufacturing should develop customized AI strategies that address their unique challenges and needs.
- AI research must become a national priority, with substantial funding for AI R&D, particularly in fundamental research.
Conclusion: India’s Moment to Lead in AI
- The convergence of government support, industry involvement, and strategic investments in AI provides India with an unprecedented opportunity to harness the power of AI.
This moment represents India’s chance to lead in the AI revolution, inspiring a new era of economic prosperity and global leadership in technology.
Read More© 2025 Civilstap Himachal Design & Development
